Lexical Analysis
Informal Sketch¶
lexical analysis 的目标就是将 string 拆分(识别)成一些 substrings (lexemes),而 substrings 又会根据用途被进一步分类 (class),例如分为 identifier、integer、keyword、whitespace 等,由 lexemes 和它对应的 class 构成的 pair 被称为 token, 最终 lexical analysis 会生成 a stream of tokens.
设计一个 lexical analyzer 可以分为以下两个步骤:
- Define a finite set of tokens
- Tokens describes all items of interest
- Choice of tokens depends on language & design of parser
- Describe which strings belong to each token
最终 lexer 会返回 token-lexeme pairs,并丢弃对 parser 无用的 pairs 例如 whitespace.
Summary
- The goal of lexical analysis is to
- Partition the input string into lexemes
- Identify the tokens of each lexeme
- Left-to-right scan => lookahead sometimes needed
Regular Languages¶
识别 lexemes 的所有 formalisms 中最流行的是 regular languages.
Syntax v.s. Semantics
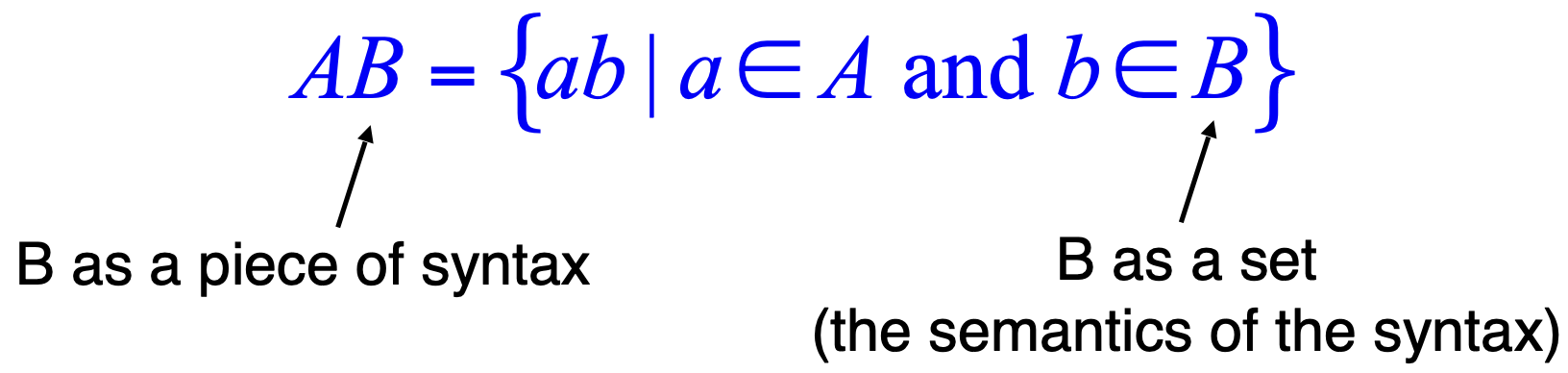
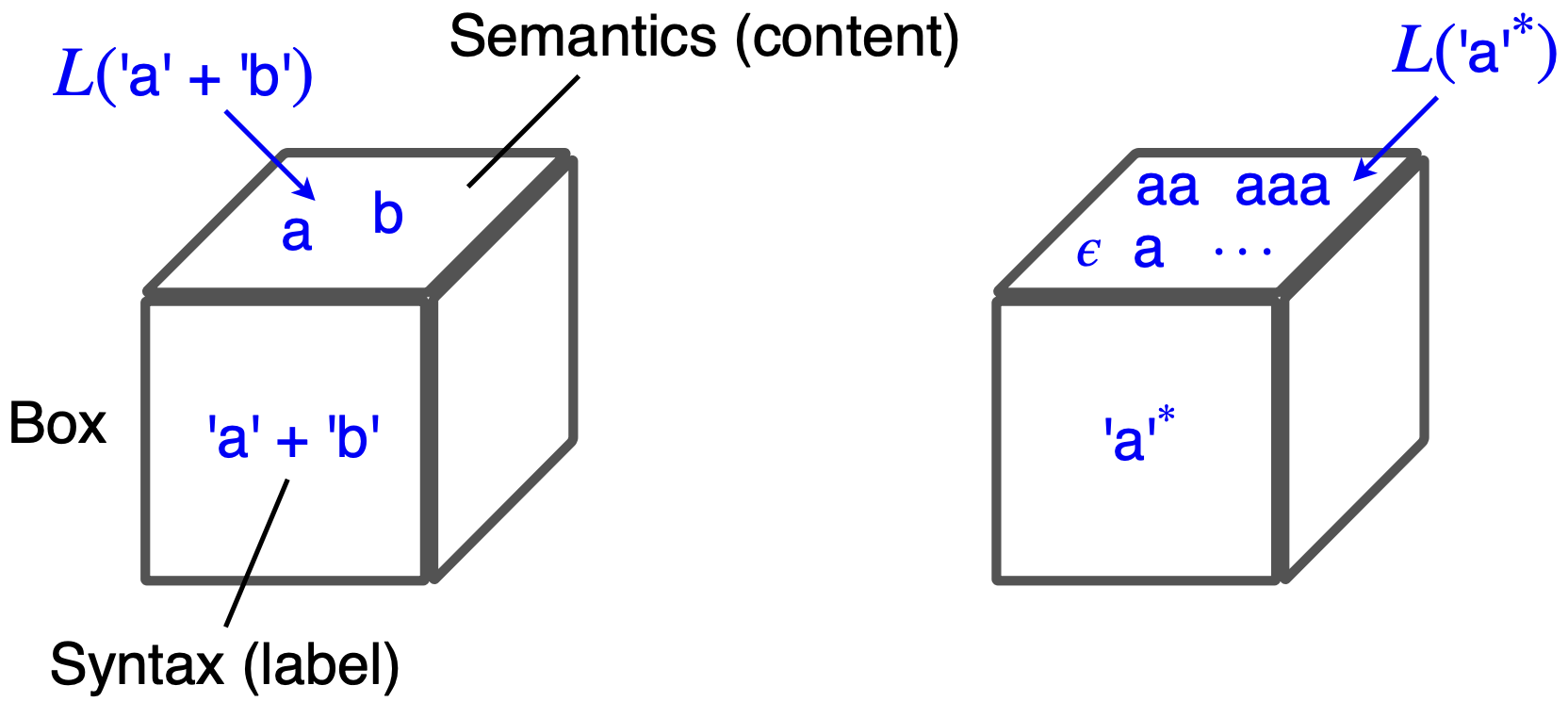
(感性理解一下)
syntax 是 expression, 通过非单射函数 \(L\) 映射到 semantics, semantics 的形式则是 a set of strings.
通常使用 regular languages 来表示 tokens, 例如:
- keyword = 'else' + 'if' + 'begin' + ...
- integer = digit digit* = digit+
- digit = [0-9]
- identifier = letter (letter + digit)*
- letter = [a-zA-Z]
- whitespace = (' ' + '\n' + '\t')+
Implementation¶
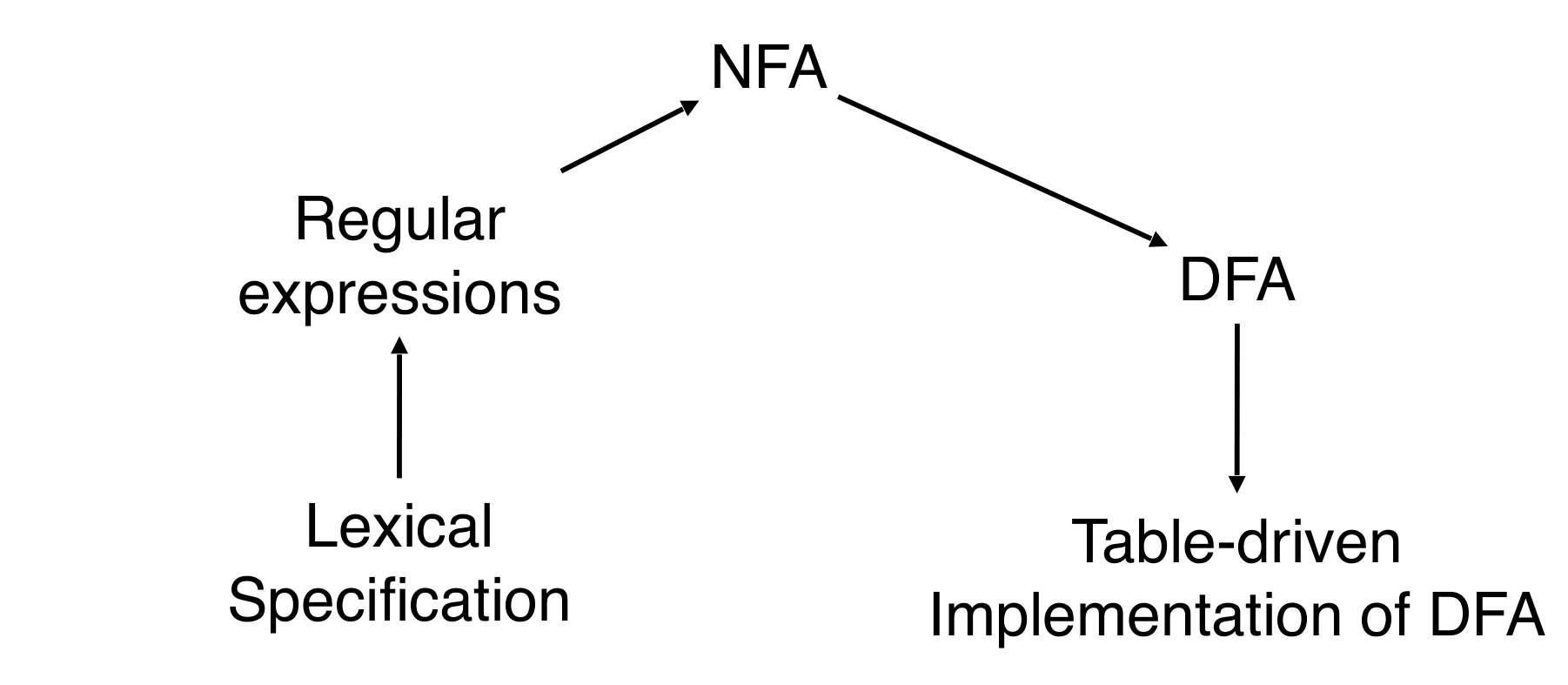
Lexical Specification → Regex:
- 每个 token 用一个 regex 表示
- 构造 R 来匹配所有 token 包含的 lexemes
- 设 input string 为 \(x_{1} \dots x_{n}\), for 循环检查是否有 \(x_{1} \dots x_{i} \in L(R)\)
- 多个满足条件的 \(i\), 选最大者 ("maximal munch")
- 若不存在这样的 \(i\), 单独列一个 rule 给这种 "bad" strings, 并列在最后(lowest priority)
- 若是,则有 \(x_{1}\dots x_{i} \in R(j)\) for some \(j\)
- \(x_{1}\dots x_{i}\) 匹配到多个 \(j\), 则选择较小的(listed first)
- 从 input string 中移除前缀 \(x_{1} \dots x_{i}\) 然后回到 (3)
finite automata 见 Automata and Language Theory.
Regex → NFA:
- 给每种 rexp 都定义一个 NFA
- \(\epsilon\):
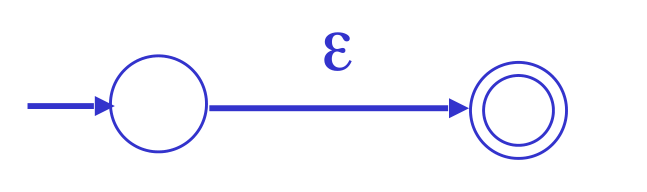
- 'a':
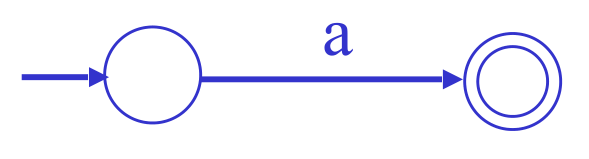
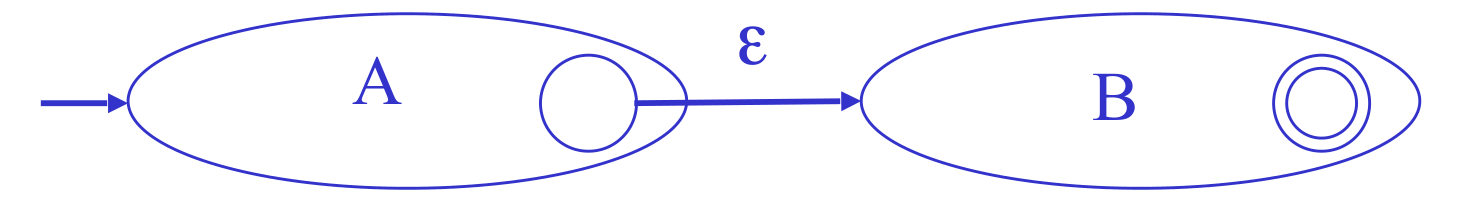
- AB:
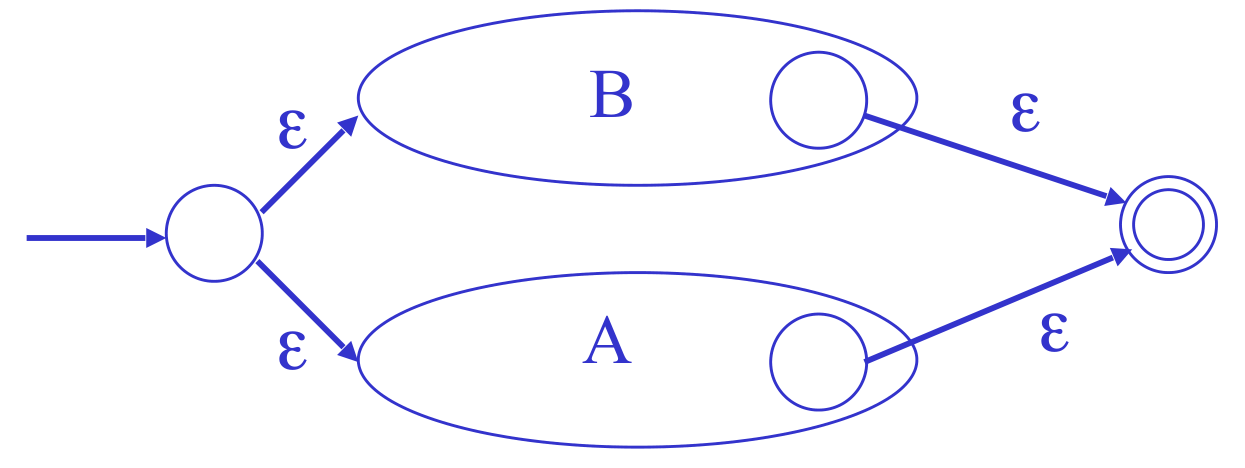
- A + B:
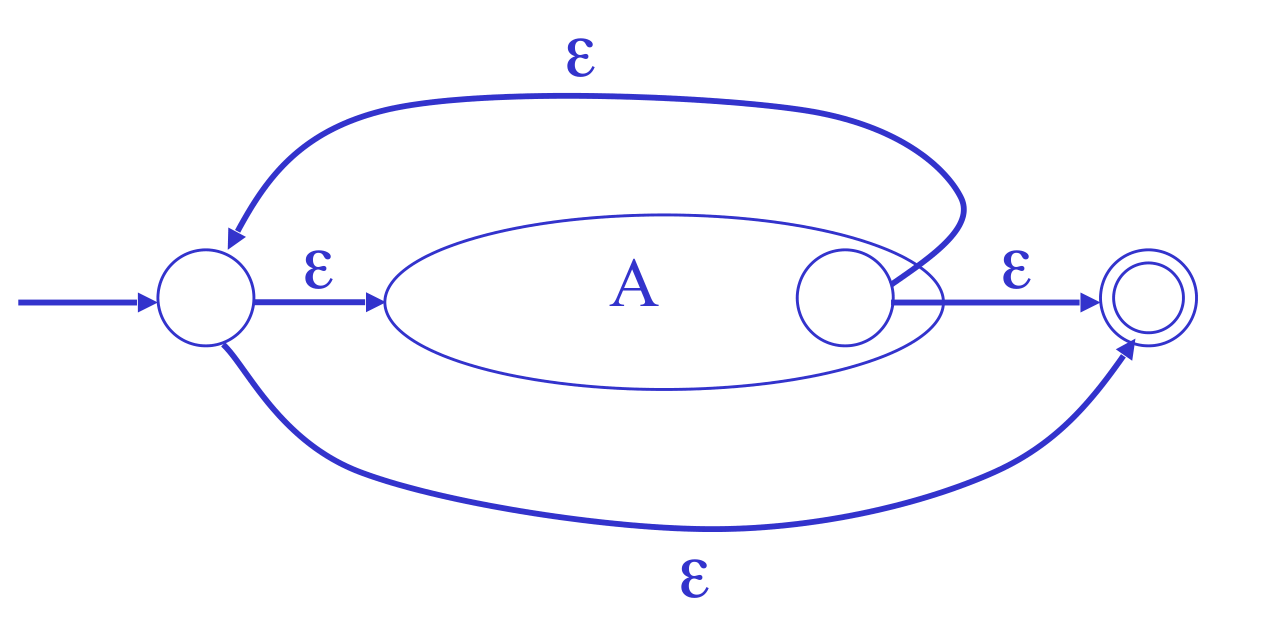
- A*:
- \(\epsilon\):
- regex 是 rexp 的组合,相同的方法将 NFAs 也组合在一起即可
NFA → DFA (optional):
- 模拟 NFA
- DFA 的每个 state 对应 NFA state 的非空子集
- 子集大小上界 \(2^n - 1\)
- start state 则是 NFA 的 start state 及其 \(\epsilon\)-moves 能到达的 state 的集合
- 当且仅当满足下列条件时在 DFA 添加 transition \(S \xrightarrow{a} S'\):
- \(S'\) 是 \(S\) 中任意 NFA state 能在 input \(a\) 后到达的所有 NFA state 的集合
DFA → Tables:
- DFA 可以用 2 维 table 表示
- 一维 state, 另一维 input symbol
- 和数电里的状态转换表是一回事
- DFA "execution"
- 当前在 state \(S_{i}\), 读入 input \(a\), 若有
T[i, a] = k则转入 state \(S_{k}\)
- 当前在 state \(S_{i}\), 读入 input \(a\), 若有